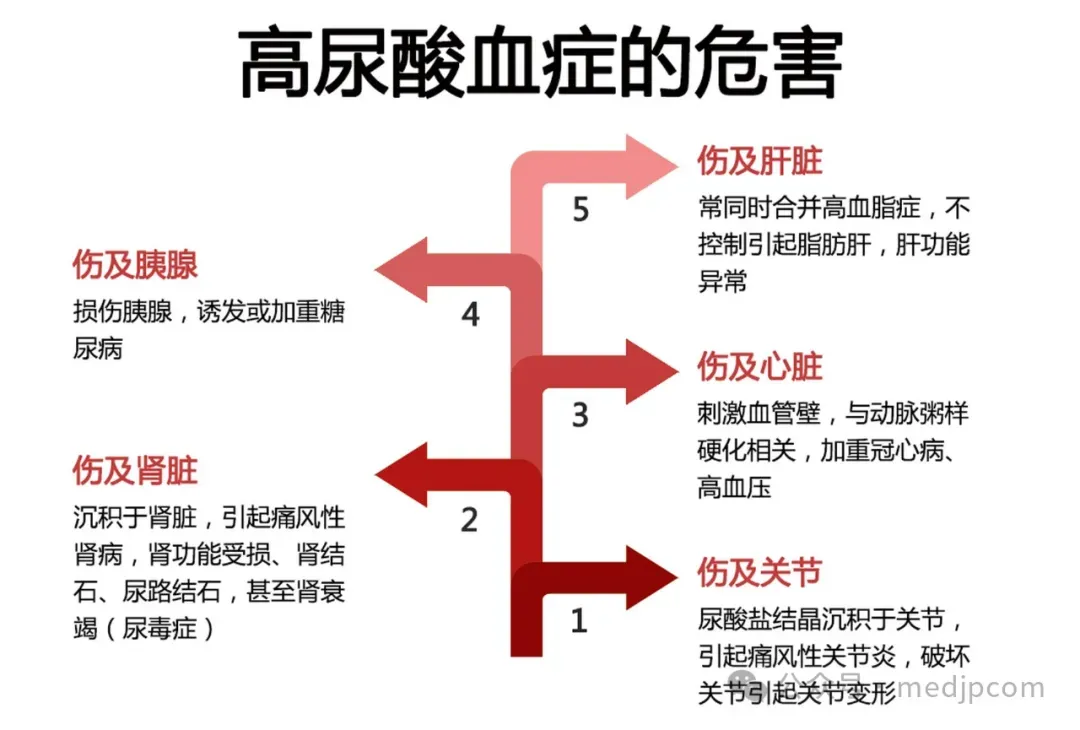
With changes in dietary patterns and increasingly diverse lifestyles, hyperuricemia and its resultant condition, gout, have become common metabolic disorders. These issues not only affect patients' daily lives but also pose significant health risks, such as kidney damage and cardiovascular complications. In recent years, the options for pharmacological treatment of hyperuricemia have become increasingly diverse. Among them, Dotinurad, a novel selective URAT1 inhibitor, has gained attention from the medical community and patients alike due to its superior uric acid-lowering efficacy and relatively fewer side effects.
In this article, we will discuss the mechanism of action, target population, and usage precautions of Dotinurad, while emphasizing the importance of scientific and informed medication use.
A Gout Medication for Hyperuricemia Treatment and Uric Acid Reduction
What Is Dotinurad?
Dotinurad is a novel oral medication for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout, developed by Fuji Pharma in Japan and launched in 2020. As a selective URAT1 inhibitor, it reduces uric acid reabsorption in the kidneys by targeting the urate transporter protein URAT1, effectively lowering serum uric acid levels.
The innovation of Dotinurad lies in its high selectivity for URAT1, without affecting other uric acid-related transporters (such as ABCG2 and OAT1/3). This unique feature not only enhances its uric acid-lowering efficacy but also reduces the risk of potential side effects.
Mechanism of Action
Precise Inhibition of URAT1
In the proximal tubules of the kidney, URAT1 is responsible for uric acid reabsorption. Dotinurad selectively inhibits URAT1, promoting uric acid excretion and significantly reducing serum uric acid levels.
Reduced Risk of Side Effects
Dotinurad has minimal impact on other uric acid transporters (e.g., ABCG2, OAT1/3), protecting kidney function while avoiding metabolic disturbances often associated with non-selective inhibitors.
Target Population and Dosage
Target Population
Patients with hyperuricemia, especially those with gout symptoms.
Patients who do not respond well to or cannot tolerate other uric acid-lowering medications.
Dosage and Administration
Dotinurad is an oral medication with the following recommended usage guidelines:
Initial Dose: 0.5 mg once daily.
Maintenance Dose: 2 mg once daily, adjustable based on serum uric acid levels and patient condition.
Maximum Dose: 4 mg once daily; exceeding this dose is not recommended.
Note: Regular monitoring of serum uric acid levels is necessary during treatment to ensure efficacy and safety.
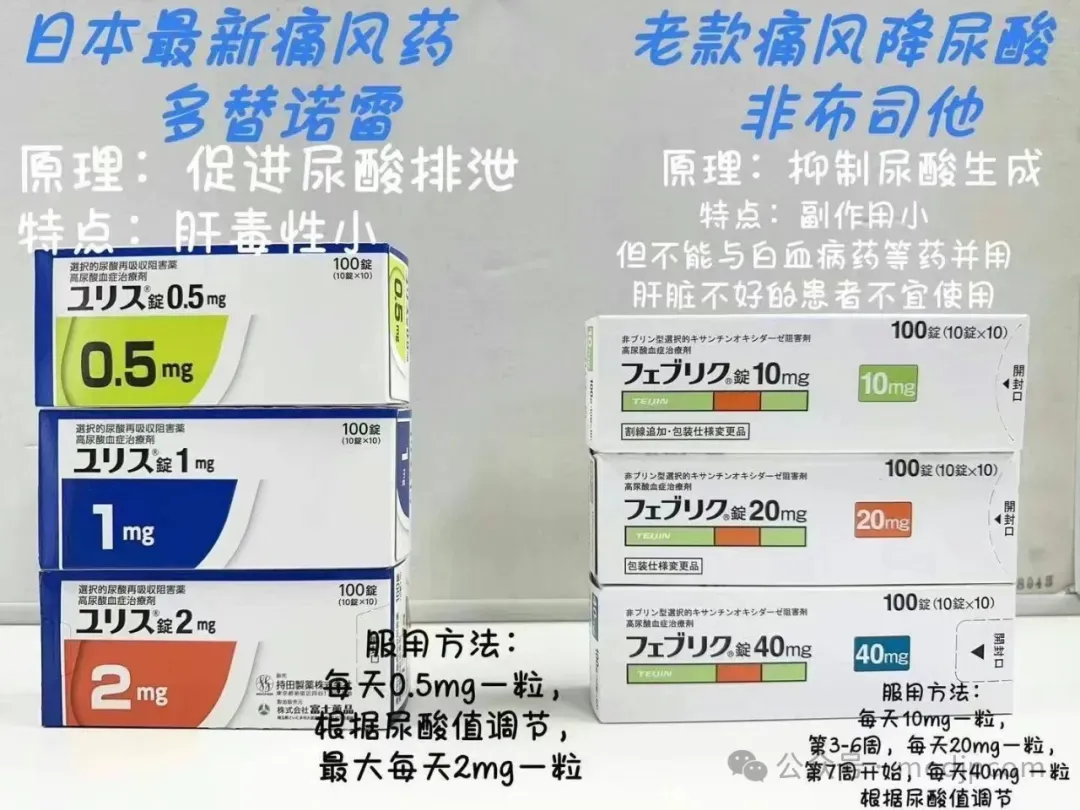
Comparison Between Dotinurad and Febuxostat
1. Drug Classification and Mechanism of Action
Dotinurad (URAT1 Inhibitor)
Classification: Urate Transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitor.
Mechanism: Inhibits the reabsorption of uric acid in renal tubules by targeting the URAT1 receptor, promoting uric acid excretion via the kidneys.
Primary Use: Effective for hyperuricemia caused by reduced uric acid excretion.
Febuxostat (XO Inhibitor)
Classification: Xanthine Oxidase (XO) inhibitor.
Mechanism: Reduces uric acid production by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity.
Primary Use: Suitable for hyperuricemia caused by excessive uric acid production or mixed causes.
2. Target Populations
Dotinurad
Suitable for patients with mild kidney impairment.
Particularly effective in hyperuricemia caused by impaired uric acid excretion.
Febuxostat
Suitable for patients with moderate to severe kidney impairment.
Ideal for hyperuricemia caused by excessive uric acid production, such as in hemolysis or tumor lysis syndrome.
3. Safety and Side Effects
Dotinurad
Generally mild side effects, including slight kidney burden, headaches, and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Not recommended for patients with excessive uric acid production.
Febuxostat
Side effects include liver function abnormalities, cardiovascular risks (rare but notable), and skin rashes.
Should be used cautiously in patients at high risk of cardiovascular diseases.
4. Drug Metabolism and Excretion
Dotinurad
Excreted via the kidneys, making it highly effective for patients with normal renal function.
Febuxostat
Metabolized by the liver, ensuring safety for patients with impaired renal function.
5. Maximum Dosage
Dotinurad
Recommended maximum dose: 4 mg daily.
Febuxostat
Recommended maximum dose: 80 mg daily (up to 120 mg for some patients).
Selection Guidelines
Choose Dotinurad: For patients with reduced uric acid excretion and relatively normal kidney function.
Choose Febuxostat: For patients with excessive uric acid production or moderate to severe kidney impairment.
Note: Medication choice should be based on uric acid type, kidney function, and overall health factors, determined through a comprehensive medical evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Precautions and Risk Alerts
Although Dotinurad is highly effective for lowering uric acid levels, consider the following:
Follow Medical Advice
Use the medication strictly under medical supervision, especially regarding dosage adjustments and treatment duration tailored to individual needs.
Regular Monitoring
Monitor serum uric acid levels periodically to prevent acute gout attacks triggered by rapid uric acid reduction.
Contraindications and Adverse Reactions
Contraindications: Not suitable for individuals allergic to Dotinurad or its components, those with severe renal impairment, pregnant women, or breastfeeding mothers.
Possible Side Effects: Mild gastrointestinal discomfort and headaches. Report severe reactions to a doctor promptly.
Combining Healthy Lifestyle with Medication
To optimize uric acid management, incorporate a healthy lifestyle:
Reduce high-purine foods.
Engage in moderate exercise.
Avoid alcohol.
Scientific Medication Tips
Hyperuricemia and gout are chronic conditions requiring long-term, systematic management. While Dotinurad offers a promising solution with high efficacy and safety, it is not suitable for every patient.
Recommendations:
Undergo a thorough medical evaluation to confirm indications before starting medication.
Follow the prescribed dosage and avoid altering or discontinuing treatment without medical advice.
Regularly review progress with your doctor and adjust treatment plans if needed.
Choosing Optimal Treatment for a Healthier Life
The introduction of Dotinurad has provided a new treatment option for patients with hyperuricemia and gout. Its precise mechanism of action and favorable safety profile mark a significant breakthrough in uric acid-lowering therapies. However, proper use under medical supervision is essential to ensure effectiveness and safety.
By combining scientific treatment with a healthy lifestyle, patients can better manage uric acid levels, improve quality of life, and achieve long-term health goals.
